About Conference
Welcome to the 19th European Diabetes and Endocrinology Congress (Euro Endocrinology 2026). This unique event highlights the diverse perspectives and advancements in diabetes and endocrinology. Healthcare professionals, including diabetes specialists, endocrinologists, nurses, and medical experts from around the world, are expected to attend this two-day conference. Medical professionals and healthcare providers recognize that preventing endocrine disorders is crucial to improving global health outcomes. According to recent statistics, the number of individuals affected by these conditions is projected to rise significantly in the coming years. In response to this growing challenge, we are organizing the 19th European Diabetes and Endocrinology Congress, scheduled for March 09–10, 2026, in London, UK, to promote awareness and foster research aimed at developing practical solutions.
The Organizing Committee warmly invites participants from across the globe to join this annual flagship event under the theme: “Innovations and Insights: Shaping the Future of Endocrine and Diabetes Care.” Euro Endocrinology 2026 will focus on the latest and most exciting breakthroughs in all areas of diabetes and endocrinology. It aims to share knowledge and facilitate collaboration among endocrinologists, diabetes experts, researchers, professors, healthcare professionals, scholars, business leaders, and industry representatives. The conference will also feature opportunities for institutions and companies to present their services, products, innovations, and research findings.
In support of advancing patient care, this activity is planned and implemented by Conference Series LLC Ltd in collaboration with the Center for Education Development (CED). CED is jointly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC) to provide continuing education for healthcare teams.
Sessions/Tracks
Diabetes is a chronic
metabolic disease characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insulin deficiency, insulin resistance, or both. The main types are Type 1, Type 2, and
gestational diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Management involves lifestyle changes, blood sugar monitoring, medications, and insulin therapy when necessary. Preventive care and early intervention are key to reducing complications. Advances in treatment, including wearable devices and innovative therapies, are improving patient outcomes.
Diabetes remains a significant global health challenge, requiring continuous research, education, and healthcare innovation.
Endocrinology is the branch of medicine focusing on the endocrine system, which regulates hormones controlling metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
Endocrinologists diagnose and treat disorders such as diabetes, thyroid diseases, adrenal disorders, osteoporosis, and hormonal imbalances. Hormones act as chemical messengers, and disruptions can affect various organs and systems. Advances in endocrinology include molecular diagnostics, genetic research, and innovative therapies improving patient care. The field also explores the complex interactions between hormones, the immune system, and chronic diseases. With the global rise in endocrine disorders,
endocrinology plays a pivotal role in preventive healthcare and chronic disease management.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence but can occur at any age. Managing
Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. Modern treatments include insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and advanced insulin formulations. Research into artificial pancreas systems and immune therapies is ongoing. Early diagnosis and effective management are essential to prevent complications such as ketoacidosis,
cardiovascular disease, and nerve damage. Patient education and support are crucial components of care.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. It is commonly associated with obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predisposition. Unlike Type 1,
Type 2 diabetes often develops gradually, primarily in adults, though increasing rates are seen in younger populations. Management includes lifestyle interventions such as diet and exercise, oral medications, and in some cases, insulin therapy. Proper control helps prevent complications like neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Recent advances focus on personalized medicine, novel drug classes like GLP-1 receptor agonists, and continuous monitoring technologies, aiming to improve long-term outcomes and quality of life.
Diabetes prevention focuses on reducing the risk of developing
Type 2 diabetes through lifestyle and behavioral changes. Key strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress levels. Programs like the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) have demonstrated success in delaying or preventing onset, especially in individuals with prediabetes. Early screening and education play critical roles in prevention efforts.
Public health initiatives aim to raise awareness, reduce risk factors, and promote healthier environments. Preventive approaches not only lower healthcare costs but also improve quality of life and reduce the global diabetes burden.
Proper
nutrition is essential for managing diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels, and preventing complications. A diabetic diet emphasizes balanced meals with controlled carbohydrate intake, high-fiber foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and limited sugar and processed foods. Glycemic index and load are considered to avoid rapid glucose spikes. Personalized meal plans, portion control, and regular monitoring help maintain stable glucose levels. Nutritional counseling supports patient education on healthy eating habits and meal planning. Emerging dietary approaches, like the Mediterranean diet and plant-based diets, show promise in improving
insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular health. Consistent nutritional management is key to diabetes care.
Digital health leverages technology to enhance healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and streamline clinical workflows. It encompasses telemedicine, wearable devices, mobile health apps, and electronic health records, enabling real-time monitoring and personalized care. For diabetes and endocrine disorders, digital health tools help track glucose levels, manage medications, and support remote consultations. AI-powered analytics and decision support systems provide predictive insights, assisting in early diagnosis and prevention strategies. Digital health fosters patient engagement, promotes preventive care, and addresses healthcare accessibility challenges. With continuous technological advancements, digital health is revolutionizing chronic disease management and redefining
healthcare interactions between patients and providers.
Circadian rhythms are 24-hour biological cycles regulating sleep, metabolism, hormone release, and other physiological processes. Disruptions in circadian rhythms, such as irregular sleep patterns or shift work, can contribute to metabolic disorders like diabetes, obesity, and endocrine dysfunction. The body’s internal clock, primarily controlled by the brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus, coordinates daily patterns of glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Chronotherapy, which aligns medical treatments with circadian timing, is an emerging field. Understanding circadian biology aids in optimizing meal timing, medication schedules, and lifestyle interventions to improve
metabolic health and prevent chronic diseases. Restoring healthy rhythms promotes overall wellbeing.
Endocrine cancers originate in hormone-producing glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, and pituitary. These rare cancers include thyroid carcinoma, adrenal cortical carcinoma, and neuroendocrine tumors. Symptoms vary based on tumor location but may include hormonal imbalances, unexplained weight changes, or fatigue. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, which may involve surgery, radiation, targeted therapy, or hormone-suppressing medications. Advances in molecular diagnostics and genetic testing have improved the understanding of endocrine tumor behavior, aiding in personalized treatment planning. Research continues into novel therapies and
biomarkers, aiming to improve survival rates and minimize treatment-related side effects.
Bone health is vital for overall mobility, strength, and quality of life. Endocrine disorders such as osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism, and thyroid dysfunction can negatively affect bone density and increase fracture risk. Calcium and vitamin D intake, along with weight-bearing exercise, are essential for maintaining strong bones. Hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and parathyroid hormone play critical roles in bone remodeling and mineralization. Screening with bone density tests helps detect early bone loss, allowing timely intervention. Treatments may include bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, and newer medications targeting
bone metabolism. Promoting lifelong bone health is key to preventing disability in aging populations.
Menstrual irregularities include changes in cycle length, missed periods, heavy bleeding, or painful menstruation. They often signal underlying endocrine issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or hormonal imbalances. Stress, obesity, and excessive exercise can also disrupt menstrual cycles. Accurate diagnosis involves
hormonal evaluations, imaging studies, and medical history review. Treatment depends on the cause and may include lifestyle modifications, hormonal therapies, or medications to regulate ovulation and menstruation. Addressing menstrual irregularities is essential for reproductive health, fertility planning, and overall well-being. Regular gynecological care and early intervention help prevent long-term complications and improve quality of life.
Diabetes treatments aim to control blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve patient quality of life. Options include insulin therapy, oral hypoglycemics, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Continuous glucose monitors and insulin pumps offer advanced management for Type 1 diabetes, while newer medications provide cardiovascular and renal protection for
Type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle modifications remain a cornerstone of therapy, including diet, exercise, and weight management. Emerging treatments focus on islet cell transplantation, artificial pancreas systems, and immunotherapies. Personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs are key to optimizing outcomes and reducing the long-term burden of
diabetes.
Endocrine disorders involve the malfunction of hormone-producing glands, leading to imbalances that affect body functions. Common conditions include diabetes, thyroid disorders, adrenal insufficiency, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Symptoms vary depending on the gland affected and may include fatigue, weight changes, growth abnormalities, or reproductive issues. Diagnosis often involves blood tests, imaging studies, and
hormonal assays. Treatment may include medication, hormone replacement, lifestyle adjustments, or surgery. Advances in endocrinology have improved early detection and personalized therapies. Managing endocrine disorders requires a multidisciplinary approach to prevent complications and promote long-term health and quality of life.
Thyroid disorders involve abnormal function of the thyroid gland, affecting metabolism, energy levels, and growth. Common conditions include hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and
thyroid cancer. Symptoms range from fatigue, weight changes, and mood alterations to heart palpitations and goiter. Diagnosis involves blood tests for TSH, T3, and T4 levels, as well as imaging and biopsy when necessary. Treatments may include
thyroid hormone replacement, antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. Managing thyroid health is essential due to its widespread impact on other organ systems. Regular screening and early intervention help prevent serious complications and maintain overall wellness.
Neuroendocrinology explores the interactions between the nervous system and the
endocrine system. It focuses on how the brain regulates hormonal activity, influencing metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress responses. Disorders such as hypothalamic dysfunction, pituitary tumors, and adrenal diseases fall under this specialty. Research in neuroendocrinology has advanced understanding of hormone-related neurological conditions, including mood disorders and neurodegeneration. Diagnostic methods include hormonal testing, neuroimaging, and functional studies. Treatments may involve medications, hormone therapy, or surgical interventions. This field bridges neurology and
endocrinology, offering insights into complex diseases and fostering innovative therapies for better health outcomes.
Hormonal Replacement Therapy (HRT) involves supplementing hormones to treat deficiencies, particularly during menopause, andropause, or endocrine disorders. In women, HRT addresses symptoms like hot flashes, osteoporosis, and vaginal dryness by replacing estrogen and progesterone. In men,
testosterone therapy treats hypogonadism. HRT can also support individuals with adrenal insufficiency or transgender individuals undergoing gender-affirming care. While HRT provides significant benefits, it carries potential risks, including blood clots, cancer, or cardiovascular events, necessitating personalized risk assessments. Recent advancements focus on bioidentical
hormones and optimized delivery methods, enhancing safety and efficacy. Proper monitoring ensures therapeutic success and minimizes complications.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause insulin resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. It usually develops in the second or third trimester and affects both the mother and baby’s health. Risk factors include obesity, family history of
diabetes, and advanced maternal age. Proper management includes monitoring blood sugar, adopting a healthy diet, exercising, and sometimes using insulin therapy. If left untreated, it can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, premature birth, or
type 2 diabetes later in life. Postpartum follow-up is crucial for both mother and child to prevent long-term
metabolic health issues.
Obesity focuses on achieving sustainable weight loss to reduce the risk of related conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and joint problems. First-line interventions include dietary changes, physical activity, behavioral therapy, and psychological support. Pharmacological options, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, are used when lifestyle modifications are insufficient. In severe cases,
bariatric surgery may be recommended, which can lead to significant improvements in metabolic health. Emerging treatments target appetite regulation, metabolism, and gut hormones.
Obesity management requires a multidisciplinary approach, addressing the root causes and promoting long-term lifestyle changes to maintain weight loss and prevent comorbidities.
Innovations in
diabetes management are transforming patient care, offering advanced tools for monitoring, treatment, and prevention. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, and artificial pancreas systems provide real-time data and automated insulin delivery. New drug classes such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors improve glucose control while protecting against cardiovascular and renal complications. Digital health platforms enable remote monitoring, data sharing, and personalized care. Research into beta-cell regeneration and
gene therapy holds promise for future cures. These advancements aim to reduce the burden of diabetes, enhance quality of life, and move closer to precision medicine solutions.
Pediatric endocrinology focuses on diagnosing and treating hormonal disorders in children and adolescents. Conditions include growth disorders, Type 1 diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, adrenal diseases, and puberty-related issues. Early detection is crucial, as hormonal imbalances can affect development, growth, and long-term health. Treatment often involves hormone replacement, lifestyle counseling, and continuous monitoring to ensure proper physical and emotional development. Pediatric endocrinologists collaborate closely with families to create individualized care plans. Advances in genetics, endocrinology, and technology are improving outcomes for young patients.
Pediatric endocrine care plays a vital role in ensuring healthy transitions from childhood to adulthood.
Childhood obesity is a growing global health concern characterized by excessive body fat accumulation in children and adolescents. It increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as
Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and psychological issues like low self-esteem and depression. Contributing factors include poor dietary habits, physical inactivity, genetic predisposition, and environmental influences. Early intervention is crucial, focusing on promoting healthy eating, regular exercise, and behavioral support. Public health initiatives, school-based programs, and parental involvement play key roles in prevention and management. Addressing childhood obesity is essential to reduce long-term health risks and improve overall quality of life.
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body's cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. As a result, glucose cannot enter cells efficiently, causing the pancreas to produce more insulin to compensate. Over time, this leads to elevated insulin and
blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing
type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Insulin resistance is commonly linked to sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, obesity, and genetics. Early detection through lifestyle interventions—such as weight loss, exercise, and balanced nutrition—can significantly reduce progression to diabetes and improve
metabolic health.
Market Analysis
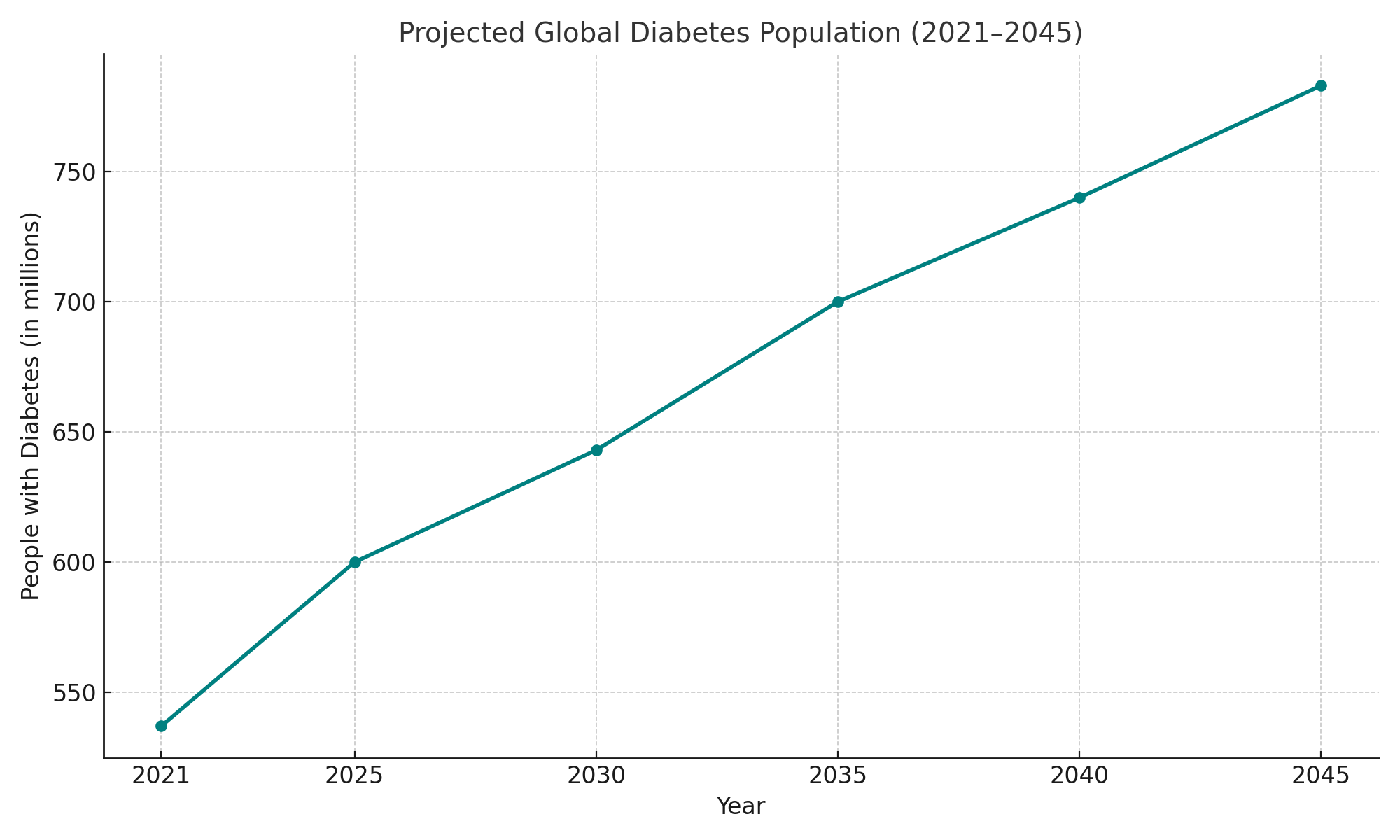
The global diabetes and endocrinology market is witnessing significant growth due to the rising prevalence of diabetes, hormonal disorders, obesity, and lifestyle-related diseases. According to the International Diabetes Federation, over 537 million adults were living with diabetes in 2021, a number projected to reach 643 million by 2030 and 783 million by 2045. Type 2 diabetes dominates the global burden, largely driven by sedentary lifestyles, poor nutrition, and aging populations. The endocrinology segment encompasses a wide array of hormonal disorders including thyroid diseases, adrenal dysfunction, growth hormone imbalances, and metabolic syndrome. Increasing awareness, better diagnostic tools, and personalized treatment plans have enhanced disease management in both developed and developing countries.
Technological advancements are playing a vital role in shaping this market. Innovations in insulin delivery systems, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), artificial pancreas devices, and mobile health (mHealth) apps are driving patient-centric care. Pharmaceutical companies are investing in novel drug classes such as SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and combination therapies that show improved glycemic control and cardiovascular benefits.
Regionally, North America holds the largest market share due to high healthcare spending, while the Asia-Pacific region is growing rapidly due to urbanization, lifestyle changes, and expanding healthcare infrastructure. Government initiatives and international collaborations are also supporting awareness, screening, and early diagnosis programs.
The global diabetes and endocrinology market is expected to exceed USD 100 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6–7%. As the burden of endocrine and metabolic disorders rises, there is a strong demand for multidisciplinary approaches integrating endocrinology, nutrition, digital health, and patient education. Conferences, research collaborations, and industry-academic partnerships will continue to play a pivotal role in advancing this sector.
Why to attend
19th European Diabetes and Endocrinology Congress gives you an opportunity to broaden your thinking and knowledge by listening to ideas and theories and recent developments in diabetes & endocrinology.
Euro Endocrinology 2026 conference can give you a wonderful opportunity to meet and interact with fellow researchers, experts across the World. It also allows you to meet new people.
Benefits of attending:
1. Learn from Top Professionals all over the world.
2. be familiar with the latest trends and challenges within your sector.
3. Share your research with top professors and get instant answers to your queries.
4. Participate in panel discussion session including live Q&A
This Euro Endocrinology 2026, will be a truly international event; we expect to welcome healthcare professionals from over 100 countries. We also have global faculty who are leading experts in their fields. Gain valuable awareness from these prominent professionals from skilled institutions.
Benefits of Joining Conference:
-
Get your abstract published with DOI
-
Get Certified for your participation
-
Reduced Costs Affordability
-
Knock Down Geographical Barriers
-
Convenience from comfort of your own home or from work
-
They’re Archived: Ability to view events in the recording
-
Great resource for learning new career skills
-
Learn from the Pros
-
Global exposure to your research
-
Make new connections
-
Significant time saving
-
Increased engagement
-
Wider Reach
-
More Engaging
-
Position yourself as the expert
Salient features
-
Keynote speeches and plenary talks by researchers all over the globe
-
Opportunity to meet globe expert’s in regenerative medical science
-
Posters, e-posters and video presentation by research community
-
International Certification by Organizing Committee
-
Publishing accepted abstracting International Journals
-
The study provides an in-depth analysis of the global Cardiology market
Target Audience
-
Endocrinologists
-
Diabetes experts
-
Dietitian
-
Students
-
Researchers
-
Professors
-
Healthcare professionals
-
Scholars
-
Business leaders
-
Industry representatives
CME & CPD Credits
CME Credits:
Continuing Medical Education (CME) refers to a specific form of continuing education that helps medical professionals to maintain competence and learn about new and developing areas of their field. Conference Series Conferences are recognised and accredited with CME credits to enhance the professional abilities and skills of participants. CME credits are important to physicians because they require a specified number of credits annually to maintain medical licenses. CME credits are authorized by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education. Attending CME accredited conference is beneficial and valuable to physicians and other medical professional as it is a source of constant improvement that ultimately improves their medical practice, and keeps them up-to-date on the latest technologies, advancements, treatments, etc. Speaking at CME activities can also be a great stage for clinical medical professionals to share their expertise and increase their distinction in their specialty.
CE Credits:
Continuing Education (CE) credit is a measure used in continuing education programs to assist the professional to maintain his or her license in their profession. Conference Series Conferences provides ample opportunities to acquire CE credits. CE can open up previously closed doors and lead to better job opportunities. CE usually refers to college courses or other vocational training obtained by older adults or working professionals. CE credits work as carrier promoter and hold great value in medical, clinical and other areas of research even after completion of degrees in concerned field of research. It is pivotal in today’s world to get updated information on your field of research and profession. Attending Continuing Education Conferences can help expand your network and make connections that could translate into profitable relationships or job opportunities down the line. It also plays a vital role in recruiting new team members for an employer with open positions. CE helps licensing organizations and professional membership groups. Continuing Education promotes high quality performance, keep professionals up to date with the latest advances, and provide excellent networking opportunities.
CPD Credits:
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is the holistic commitment of professionals towards the enhancement of personal skills and proficiency throughout their careers. It enables learning to become conscious and proactive, rather than passive and reactive. CPD accreditation is important because it ensures that courses provided adhere to the highest educational standards and international benchmarks of quality and learning. CPD enriches your knowledge, keeps you currently competent and is the key to career progression and professional growth. There are many advantages to carrying out CPD that includes filling gaps in your knowledge and skills to become more productive and efficient, building confidence and credibility to stand out from the crowd, achieving your career goals and demonstrating professional status. CPD hours can be earned through continuing education, leadership activities, instructional activities, completion of significant work projects, research and publications. Conference Series Conferences have been accredited with CPD credits to expedite the progress of research and industry professionals.
Past Conference Report
18th European Diabetes and Endocrinology Congress was organized during April 10-11, 2025, at Hotel Pineta Palace & Congress Centre, Rome, Italy . The conference was marked with the attendance of Editorial Board Members of supporting journals, Scientists, young and brilliant researchers, business delegates and talented student communities, who made this conference fruitful and productive, This conference was based on the theme “Current Trends, Novel Innovations and Advances in Diabetes Management” which included the following scientific tracks:
We taken the privilege of felicitating
Euro Endocrinology 2026 which will be held during March 09-10, 2026 in London, UK. We cordially welcome all the Organizing Committee, Editorial Board Members and Keynote Speakers who supported for the success of this conference, The esteemed guests, keynote speakers and researchers shared their innovative research and vast experience through their informative presentations at the podium of
Euro Endocrinology 2026 We are glad to inform that all accepted abstracts for the conference have been published in our respective journals.










